Turbo SMS
Detailed Description
Short message service is the most popular data service in mobile networks. The term SMS is usually equivalent to the text message, but in fact the text message is just a one special type of short message. In mobile networks the short messaging is used for many other activities by mobile operators - control of SIM, setting up ME configurations, data exchange between STK applications, etc.
As of standards the most important for you as STK application developer are the following:
To simplify the SMS handling for data exchange between applications we provide so called Turbo SMS or TSMS - datagram protocol similar to UDP. Its header helps Turbo to recognize and pass the message to appropriate application and also provides some security means.
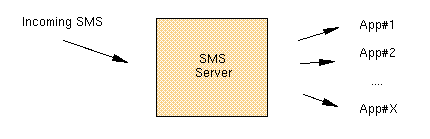
SMS Server
Turbo SMS is 8bit Class 2 (DCS=0xF6) message, i.e. SIM terminated message. PID is either 0x7f (preferred, if operators permits) or 0x00.
The first step for application to use TSMS is to register application specific tag (mime), "callback" in the following example:
In this example we registered callback application TSMS specific tag, type of message is SMS_TYPE_MSG.
The lc_Callback is the name of application the user sees in the TSMS access control.
The best place (but not required) for reg_sms_tag() is in turbo_handler(), ACTION_APP_REGISTER.
There are two types of Turbo SMS:
- Message Type
- Question-Answer (or eq. Client-Server) Type
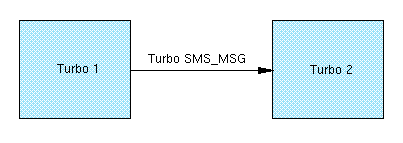
Turbo SMS Message Scenario
In the message case the first application just sends data to the same application in another Turbo, example of usage can be e.g. encrypted message.
The format of Message TSMS consist of simple header and user data. The header starts with turbo/M tag followed with application specific \0 terminated tag.

Turbo SMS Message Format
Example - Turbo 1 sending message:
u8 PROGMEM t_sms_ex[]="Example sms";
u8 PROGMEM t_ms[]="+420123456789";
{
u8 * sms=malloc(100);
u8 * p;
u8 * ms=str2msisdn(t_ms, MSISDN_ADN, MEM_R);
p=create_head_msg(sms, t_Callback_mime);
memcpy(p, t_sms_ex, sizeof(t_sms_ex));
p+=sizeof(t_sms_ex);
send_sms(sms, p-sms, ms, MSISDN_ADN, tsms_dcs(), tsms_pid(), NULL, NULL);
free(sms);
free(ms);
}
Example - Turbo 2 receiving message:
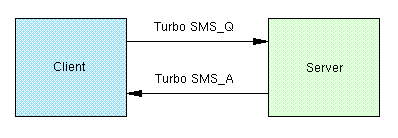
Turbo SMS Client/Server scenario
In the case of question-answer - clien/server - scenario the first application expects answer from the application in another Turbo. The real case example can be location request, question "what is your cellid?", answer "cellid".
The format of Q/A Turbo SMS is simillar to message type but there is extra 2byte sequence number:
- The purpose of sequence number is to filter out possible fake answers.
- The sequence number in answer message is copy of sequence number in question message.
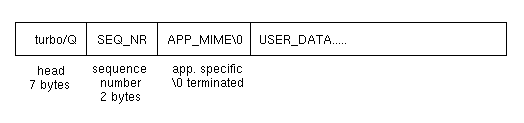
Turbo SMS Question Format
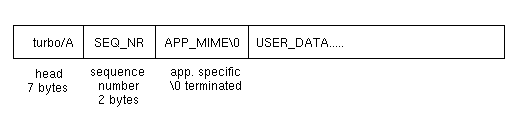
Turbo SMS Answer Format
Example - registration:
Example - Client sending question:
u8 PROGMEM t_sms_ex[]="Example sms";
u8 PROGMEM t_ms[]="+420123456789";
{
u8 * sms=malloc(100);
u8 * p;
u8 * ms=str2msisdn(t_ms, MSISDN_ADN, MEM_R);
p=create_head_q(sms, t_Position_mime, ms, MSISDN_ADN);
memcpy(p, t_sms_ex, sizeof(t_sms_ex));
p+=sizeof(t_sms_ex);
send_sms(sms, p-sms, ms, MSISDN_ADN, tsms_dcs(), tsms_pid(), NULL, NULL);
free(sms);
free(ms);
}
Example - Server receiving question and sending answer:
void pos_q_sms(u8 *s)
{
u8 * ms=msisdncpy(tpdu_seek(s,T_SMS_OA), MSISDN_SMS, MEM_R);
u8 * sms=malloc(139);
u8 * p;
p=create_head_a(sms, s);
p+=...append data, compose answer
send_sms(sms,p-sms, ms, MSISDN_SMS, tsms_dcs(), tsms_pid(), NULL, NULL);
free(sms);
free(ms);
}
Example - Client receiving answer:
To guarantee privacy the Turbo SMS handling logic allows the user to configure access rights, i.e. user can control who can access any application via TSMS.
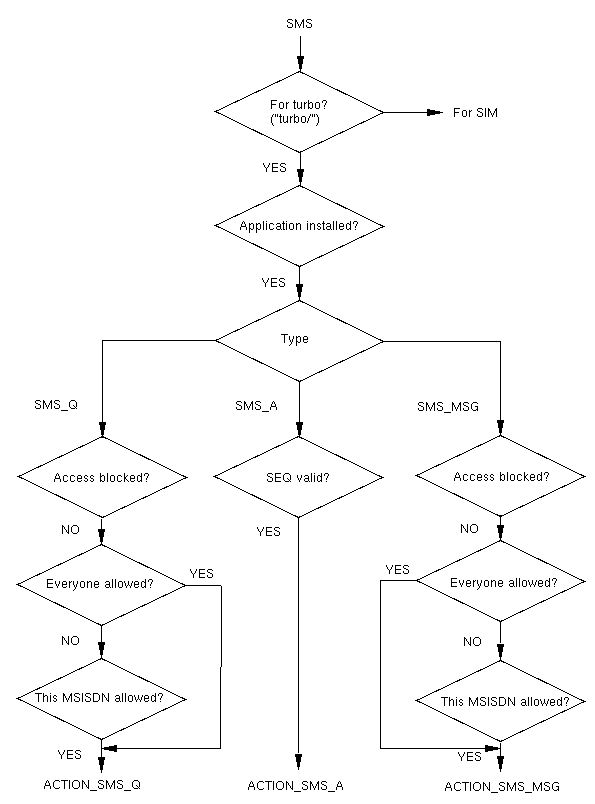
SMS processing flow
API for Turbo SMS ACL consists of TSMS_ACL * lookup_tsms_tag (const u8 *mime, u8 type) call, which returns pointer on TSMS_ACL structure for given mime/type combination. This structure contains general flags and list of numbers. The list of numbers is in form of SEdge records, see Spider for details. TSMS_ACL is stored in EEPROM and wb(), rb(), ww(), rw() calls have to be used to access/modify.
PID 0x7F indicates SIM Data Download Message, the special type of short message used for sending/receiving of SMS for STK application. In theory user should not be aware of receiving/sending of such messages (though real implementations are lame).
The Data Download Message makes it the ideal candidate for application data exchange. Unfortunately operators can block general usage of 0x7f pid and some even do. There are no technical nor security reasons for such policy, it is just a way how to treat customers.
In case 0x7f PID is blocked by operator then user can configure its Turbo to use 0x00 PID value instead. Its only drawback is that recepient ME informs user about received SMS, which can be stored in SIM SMS memory. The store behaviour - i.e. whether to store the TSMS or delete it can be also configured by recepient Turbo.
The application has access to user configured TSMS PID/DCS with the help of tsms_pid() and tsms_dcs() calls.
Data Structures
Defines
Typedefs
Functions
- u8 dcs_is_7b (u8 dcs)
- u8 dcs_7b_len (u8 len)
- u8 dcs_78 (u8 *buf, u8 nr_chars, u8 from_to)
- u8 * tpdu_seek (u8 *s, u8 tag)
- u8 reg_sms_tag (const u8 *text, const u8 *mime, u8 type)
- TSMS_ACL * lookup_tsms_tag (const u8 *mime, u8 type)
- u8 tsms_pid (void)
- u8 tsms_dcs (void)
- u8 * create_head_q (u8 *buf, const u8 *mime, const u8 *msisdn, u8 msisdn_type)
- u8 * create_head_a (u8 *buf, u8 *msg)
- u8 * create_head_msg (u8 *buf, const u8 *mime)
- u8 * skip_head (u8 *msg)
Define Documentation
| #define DCS_GSM_7_BIT_ALPHA
|
|
|
|
Indicates Status Report Request |
|
|
Indicates Turbo SMS Message Type. |
|
|
Indicates Turbo SMS Question/Answer Type. |
|
|
Any Address, substitute for Recipient Address, Destination Address, Originating Address, ref. Ref. 03.40. |
| #define TP_MTI_DELIVER_REPORT
|
|
| #define TP_MTI_STATUS_REPORT
|
|
| #define TP_MTI_SUBMIT_REPORT
|
|
|
|
If set then all incoming TSMS of given tag are trashed. This is the first check when TSMS is received. |
| #define TSMS_ACL_EVERYONE
|
|
|
|
If set then access list (list of allowed numbers) is not checked and TSMS is passed to application. |
Typedef Documentation
|
|
Turbo SMS Access Control List. |
Function Documentation
| u8* create_head_a |
( |
u8 * |
buf, |
|
|
u8 * |
msg |
|
) |
|
|
|
|
Create answer Turbo SMS header based on received question Turbo SMS. - Parameters:
-
| buf | pointer on buffer to create answer head in. |
| msg | pointer on question Turbo SMS. |
- Returns:
- pointer to buffer pointing after the header.
- Examples:
-
certs.c, and pos.c.
|
| u8* create_head_msg |
( |
u8 * |
buf, |
|
|
const u8 * |
mime |
|
) |
|
|
|
|
Create message Turbo SMS header. - Parameters:
-
| buf | pointer on buffer to create answer head in. |
| mime | application specific header indicator (type), can be stored in EEPROM, RAM or PROGMEM. |
- Returns:
- pointer in buffer pointing after the header.
- Examples:
-
callback.c, and tsmsacl.c.
|
| u8* create_head_q |
( |
u8 * |
buf, |
|
|
const u8 * |
mime, |
|
|
const u8 * |
msisdn, |
|
|
u8 |
msisdn_type |
|
) |
|
|
|
|
Create question Turbo SMS header. - Parameters:
-
| buf | pointer on buffer to create buffer in. |
| mime | pointer on application specificic header tag, stored in RAM, EEPROM or PROGMEM. |
| msisdn | pointer on MSISDN, stored in RAM, EEPROM or PROGMEM. |
| msisdn_type | MSISDN type, MSISDN_ADN, MSISDN_SMS. |
- Returns:
- pointer in buffer pointing after the header.
- Examples:
-
certs.c, and pos.c.
|
| u8 dcs_78 |
( |
u8 * |
buf, |
|
|
u8 |
nr_chars, |
|
|
u8 |
from_to |
|
) |
|
|
|
|
Converts packed 7b to/from unpacked 8b coding. - Parameters:
-
| buf | pointer on buffer where input/output is stored. For 7b to 8b you must guarantee that there is enough space for nr_chars. |
| nr_chars | number of chars (either in 7b or 8b coding) |
| from_to | either DCS_7_TO_8 or DCS_8_TO_7 |
- Returns:
- number of valid bytes in buffer.
|
|
|
Returns number of septets fitting into len bytes (i.e. len*8/7). - Parameters:
-
- Returns:
- len_7b number of septets fitting the
len bytes
|
|
|
Checks whether dcs is 7b coding or not, ref. Ref. 03.38. - Parameters:
-
- Returns:
- 0 if not 7b, 1 if 7b coding
|
|
|
Returns the Turbo SMS Access Control List for requested tag (mime). NULL if not found. The ACL is stored in EEPROM.
- Parameters:
-
- Returns:
- ACL struct stored in EEPROM or NULL if not found
- See also:
- TSMS_ACL_BLOCKED, TSMS_ACL_EVERYONE
- Examples:
-
tsmsacl.c.
|
| u8 reg_sms_tag |
( |
const u8 * |
text, |
|
|
const u8 * |
mime, |
|
|
u8 |
type |
|
) |
|
|
|
|
Used for registration of Turbo SMS application specific tag. - Parameters:
-
| text | name of application shown user in Turbo SMS access control (can be from RAM, EEPROM, PROGMEM) |
| mime | application specific Turbo SMS type (can be from RAM, EEPROM, PROGMEM) |
| type | type of Turbo SMS, SMS_TYPE_MSG or SMS_TYPE_QA |
- Returns:
- NO_ERROR or ERR_NO_EEPROM
- Examples:
-
callback.c, certs.c, pos.c, and tsmsacl.c.
|
| u8* skip_head |
( |
u8 * |
msg |
) |
|
|
|
|
Skip Turbo SMS header and point on data. - Parameters:
-
| msg | pointer on (Turbo) SMS, RAM only. |
- Returns:
- pointer on data, if not Turbo SMS then on UDL element.
- Examples:
-
certs.c, and pos.c.
|
| u8* tpdu_seek |
( |
u8 * |
s, |
|
|
u8 |
tag |
|
) |
|
|
|
|
Seek tag (element) in TPDU, i.e. SMS with all elements, Ref. 03.38. - Parameters:
-
| s | pointer of TPDU (RAM only) |
| tag | element to seek, can be T_SMS_PID, T_SMS_DCS, T_SMS_SCTS, T_SMS_UDL, T_SMS_UD, T_SMS_MR, T_SMS_VP, T_SMS_DT, T_SMS_ST, T_SMS_AA |
- Returns:
- NULL if not found, pointer on element if found
- Examples:
-
callback.c, and certs.c.
|
|
|
Returns preferred Turbo SMS DCS related to tsms_pid(). It is 0xF6. - Returns:
- TSMS DCS.
|
|
|
Returns user configurable Turbo SMS (or Data Download in general) PID. Usually 0x7f but can be also 0x00 if operators limits the 0x7f usage. - Returns:
- user preferred TSMS PID.
|
| Copyright © 2004-2006 BLADOX
| Turbo version 1.2
|







